Circle Chain: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Asset Management System
Abstract
Circle Chain is a cloud-based distributed peer-to-peer system for managing virtual assets including ownership and identity certificates. Unlike traditional blockchain systems that store data locally, Circle Chain leverages cloud storage to provide a more extensive and accessible blockchain and wallet service. The system allows for secure transfer of ownership and identity certificates using Circle Coin as the medium of exchange.
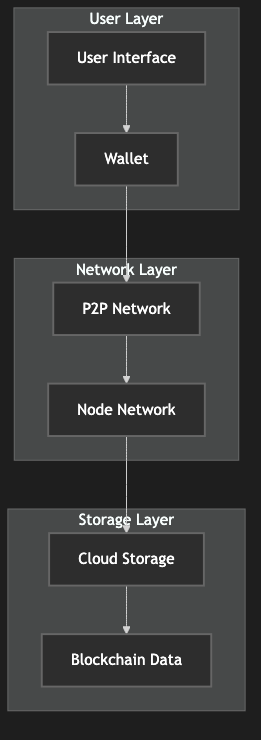
Figure 1: Circle Chain System Architecture Overview, showing the relationships between cloud storage, node network, and user interface
1. Introduction
The emergence of blockchain technology has revolutionized how we think about digital ownership and identity. Circle Chain builds upon these foundations to create a comprehensive system for managing virtual assets in a secure, distributed manner. The system uses Circle Coin as its native token to facilitate the exchange of ownership and identity certificates.
2. Transactions
2.1 Currency Transaction
Circle Chain's currency transaction system is designed to facilitate the transfer of Circle Coins between addresses. The system implements the following features:
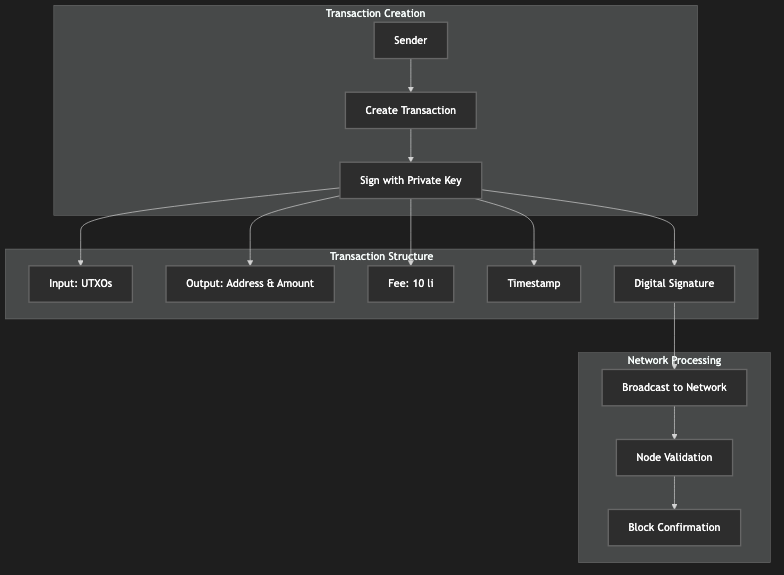
Figure 2.1: Currency Transaction Process Diagram, showing the complete transaction flow from creation to confirmation
Transaction Structure
Input: Previous transaction outputs (UTXOs)
Output: Recipient address and amount
Fee: Small amount of Circle Coins for network processing
Timestamp: Transaction creation time
Signature: Digital signature of the sender
Transaction Types
Standard Transfer: Direct transfer of Circle Coins between addresses
Multi-signature: Transactions requiring multiple signatures
Transaction Process
Creation: Sender creates transaction with recipient details
Signing: Transaction is signed with sender's private key
Broadcasting: Transaction is broadcast to the network
Validation: Network nodes validate transaction
Confirmation: Transaction is included in a block
Security Features
Double SHA-256 hashing for transaction IDs
P2PKH (Pay to Public Key Hash) for address verification
Input/output validation to prevent double-spending
Minimum fee requirement to prevent spam
Transaction Fees
Base fee: 10 li per assets transaction such as Ownership and Identity Certificates.
Size-based fee: Additional fee based on transaction size, 0 at the present.
Priority fee: Optional fee for faster processing, 0 at the present.
2.2 Ownership Certificates
Ownership certificates represent the right to possess virtual assets within the blockchain. These certificates can be transferred between addresses with a nominal fee of 10 li (Circle Chain's smallest unit). Each transfer generates a new unique ownership identifier (UID) for the recipient.
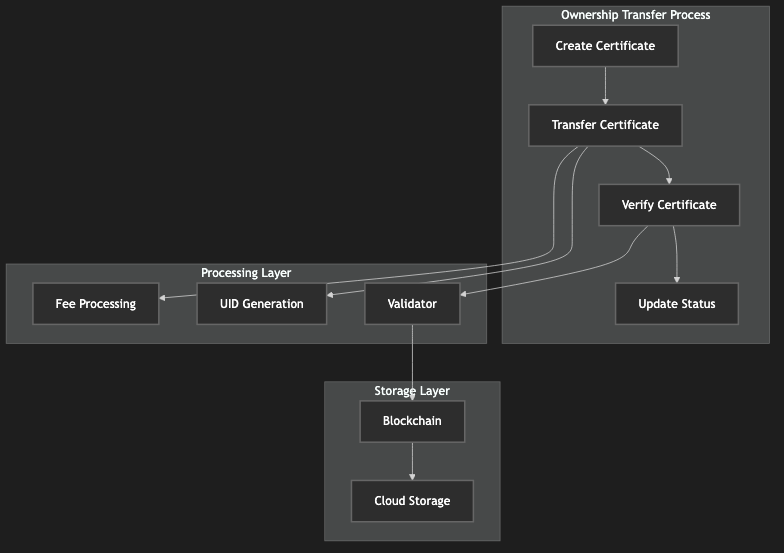
Figure 2: Ownership Certificate Transfer Process Diagram, showing the complete process and validation mechanism
2.3 Identity Certificates
Identity certificates serve as proof of identity within the blockchain ecosystem. Like ownership certificates, they can be transferred between addresses with a fee of 10 li. Each transfer creates a new unique identity identifier.
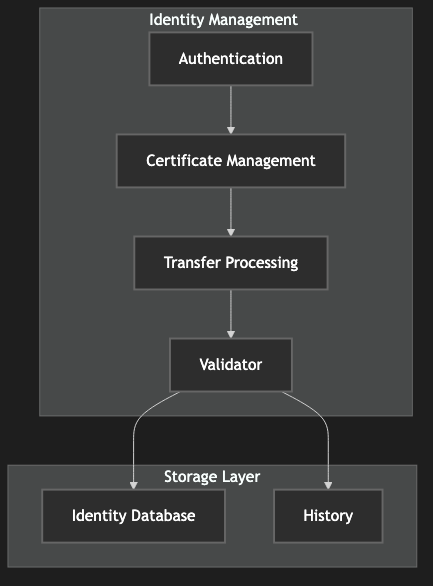
Figure 3: Identity Certificate Management System Architecture, showing the components of identity verification and management
2.4 Transfer Mechanism
The transfer system allows for flexible movement of both ownership and identity certificates:
Transfers can occur between any two different addresses
Users can transfer between their own addresses
Each transfer requires a small fee in Circle Coin
New UIDs are generated for each transfer
3. Proof-of-Work
Circle Chain implements a proof-of-work system similar to Bitcoin's, with some key differences:
Multi-threaded mining support for improved performance
Cloud-based storage of blockchain data
Configurable mining difficulty
Support for both single-thread and multi-thread mining operations
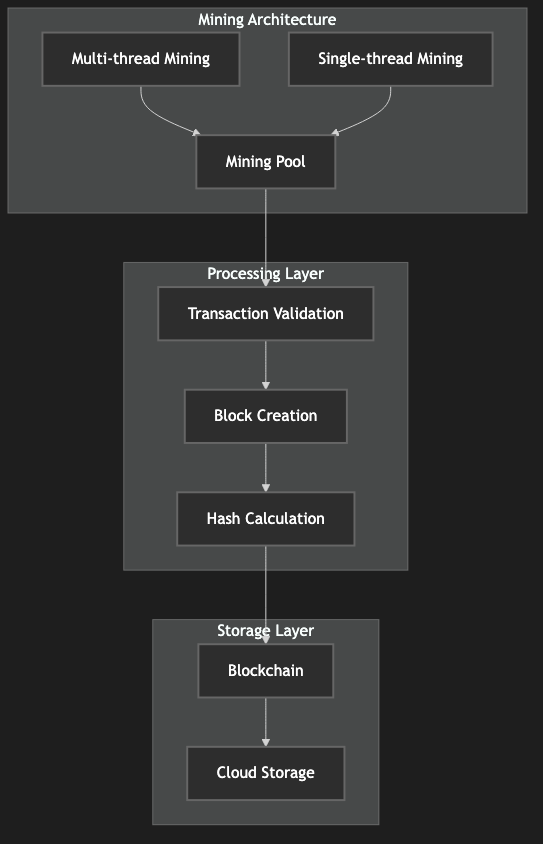
Figure 4: Circle Chain Mining Architecture, showing the implementation of single-thread and multi-thread mining
4. Network Architecture
4.1 Node Types
Circle Chain supports two primary node types:
Clouder Nodes: Handle cloud storage and API services
Miner Nodes: Participate in block creation and validation
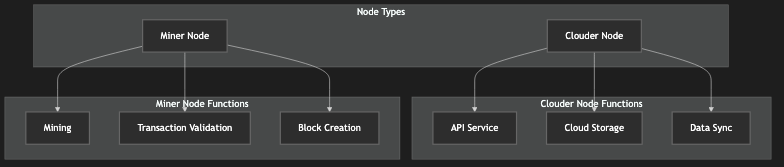
Figure 5: Node Types Diagram, showing the functions and interactions of different node types
4.2 P2P Network
The network operates on a peer-to-peer basis with:
Automatic node discovery
Heartbeat mechanism for node synchronization
Block and transaction broadcasting
Fork resolution through block tails
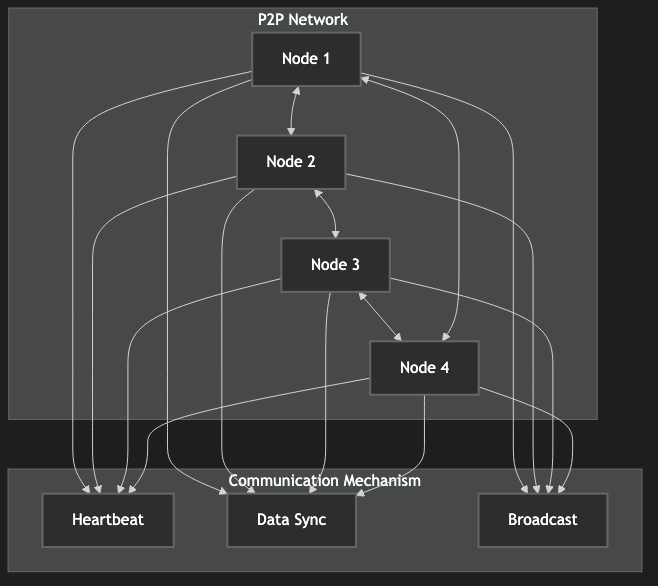
Figure 6: P2P Network Architecture Diagram, showing node communication and data synchronization mechanisms
5. Security
5.1 Cryptographic Features
Public/private key pairs for wallet addresses
P2PKH (Pay to Public Key Hash) protocol for transaction locking
RSA encryption for asset data
Double SHA-256 hashing for block and transaction IDs
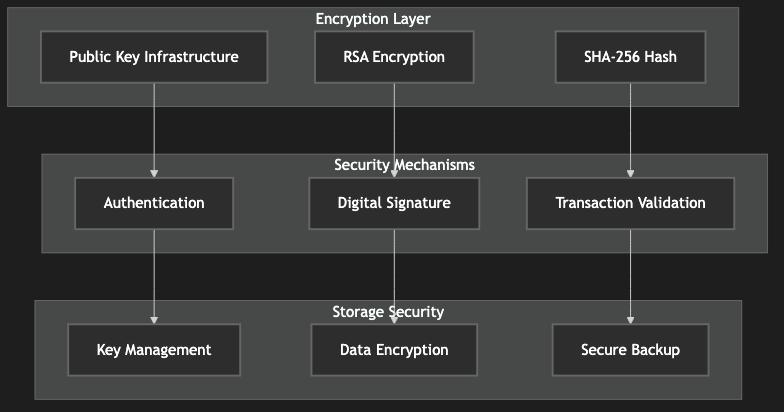
Figure 7: Security Architecture Diagram, showing the implementation of encryption and validation mechanisms
5.2 Wallet Security
Circle Chain offers two wallet types:
Cloud Wallet: Stores private keys in secure cloud servers
Local Wallet: Stores private keys locally for maximum security
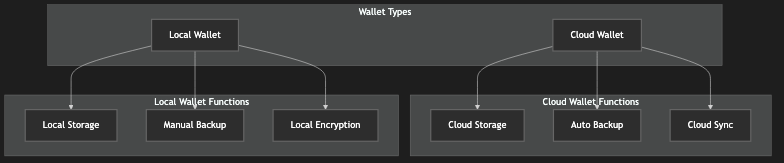
Figure 8: Wallet Architecture Diagram, showing the implementation of cloud and local wallets
6. Asset Management
6.1 Circle Coin
Circle Coin serves as the native token for:
Paying transaction fees
Exchanging ownership certificates
Transferring identity certificates
General value transfer
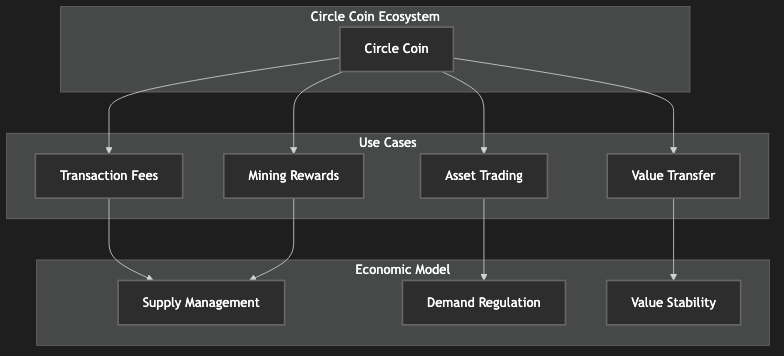
Figure 9: Circle Coin Ecosystem Diagram, showing the token's application scenarios in the system
6.2 Virtual Assets
The system supports two main types of virtual assets:
Ownership Certificates
Represent rights to virtual assets
Transferable with fees
Unique UID generation
Identity Certificates
Represent blockchain identity
Transferable with fees
Unique UID generation
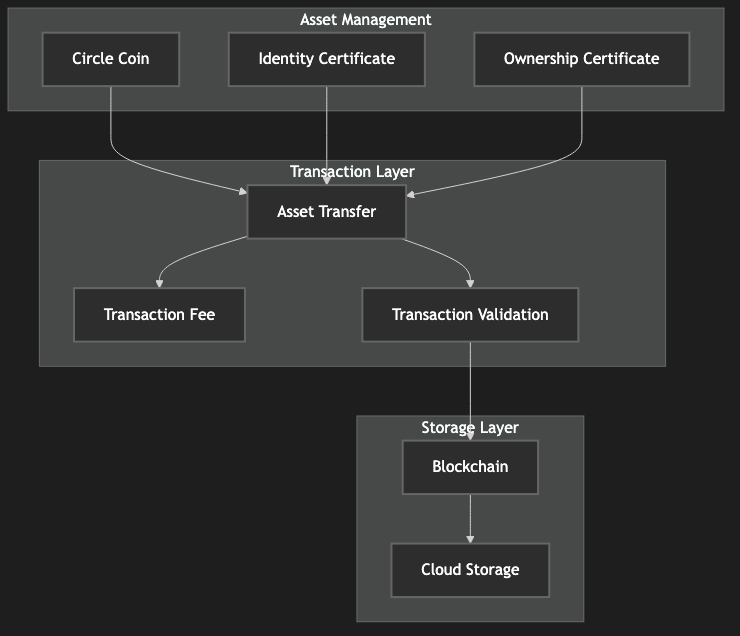
Figure 10: Asset Management Process Diagram, showing the creation, transfer, and management of virtual assets
7. Implementation
7.1 Cloud Storage
Circle Chain's cloud storage system provides:
Distributed data storage
High availability
Automatic backup
Scalable architecture
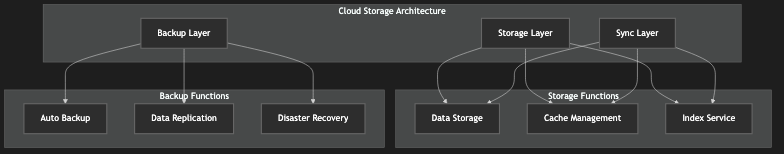
Figure 11: Cloud Storage Architecture Diagram, showing data storage and backup mechanisms
7.2 API Layer
The system exposes several API categories:
User APIs for account management
Wallet APIs for asset management
Block APIs for blockchain interaction
Clouder APIs for cloud services
Miner APIs for mining operations
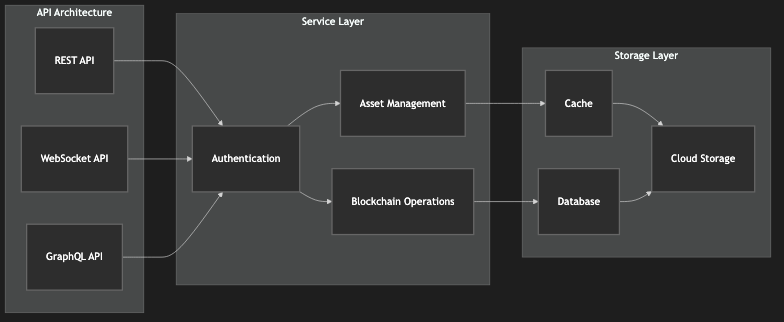
Figure 12: API Architecture Diagram, showing the functions and interactions of various API categories
8. Conclusion
Circle Chain represents a significant advancement in blockchain technology by combining the security of traditional blockchains with the accessibility and scalability of cloud computing. The system's focus on virtual asset management, particularly ownership and identity certificates, makes it uniquely suited for modern digital asset management needs.
References
[1] Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System
[2] Circle Chain Technical Documentation
[3] Blockchain Technology: Principles and Applications